
STAR Gains Access to “Wimpy” Quarks and Gluons
Low-momentum (wimpy) quarks and gluons contribute to proton spin, offering insights into protons’ behavior in all visible matter.

Low-momentum (wimpy) quarks and gluons contribute to proton spin, offering insights into protons’ behavior in all visible matter.

Researchers demonstrated record accelerating cavity performance using a technique that could lead to significant cost savings.

A first-of-its-kind computer simulation reveals self-healing cement for geothermal and oil and gas wells performs better than originally thought.
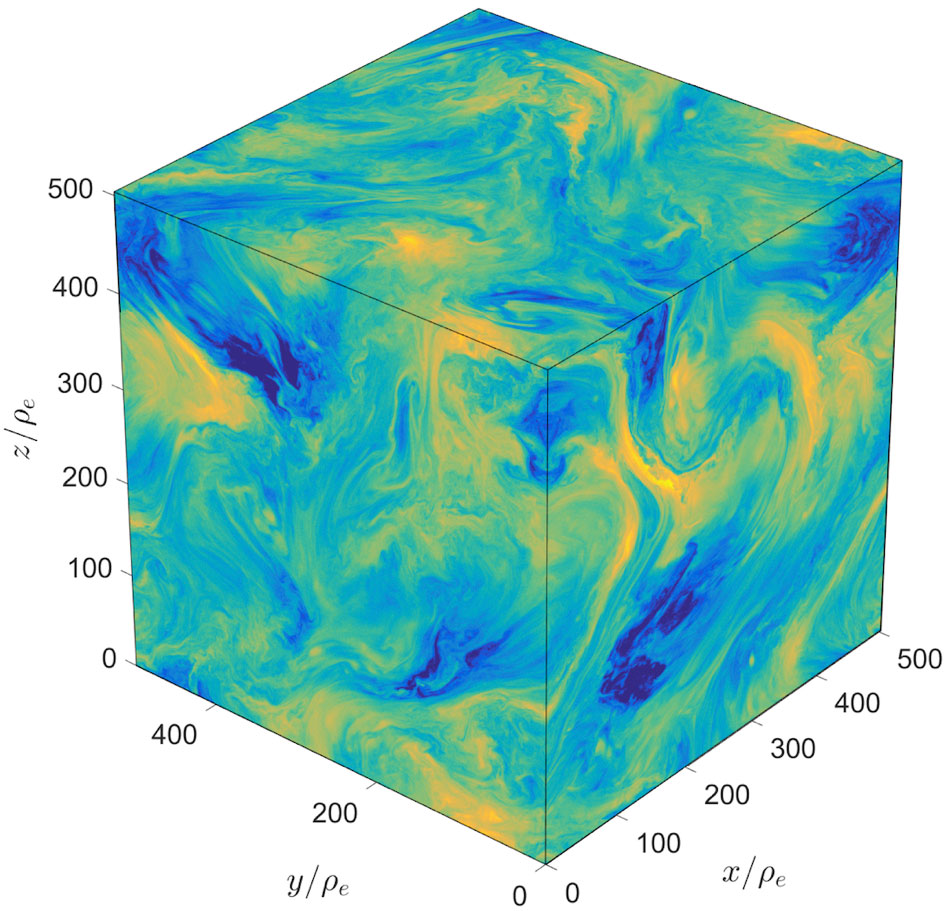
Particles act in a way that justifies extrapolating simulation results to astrophysical scales.
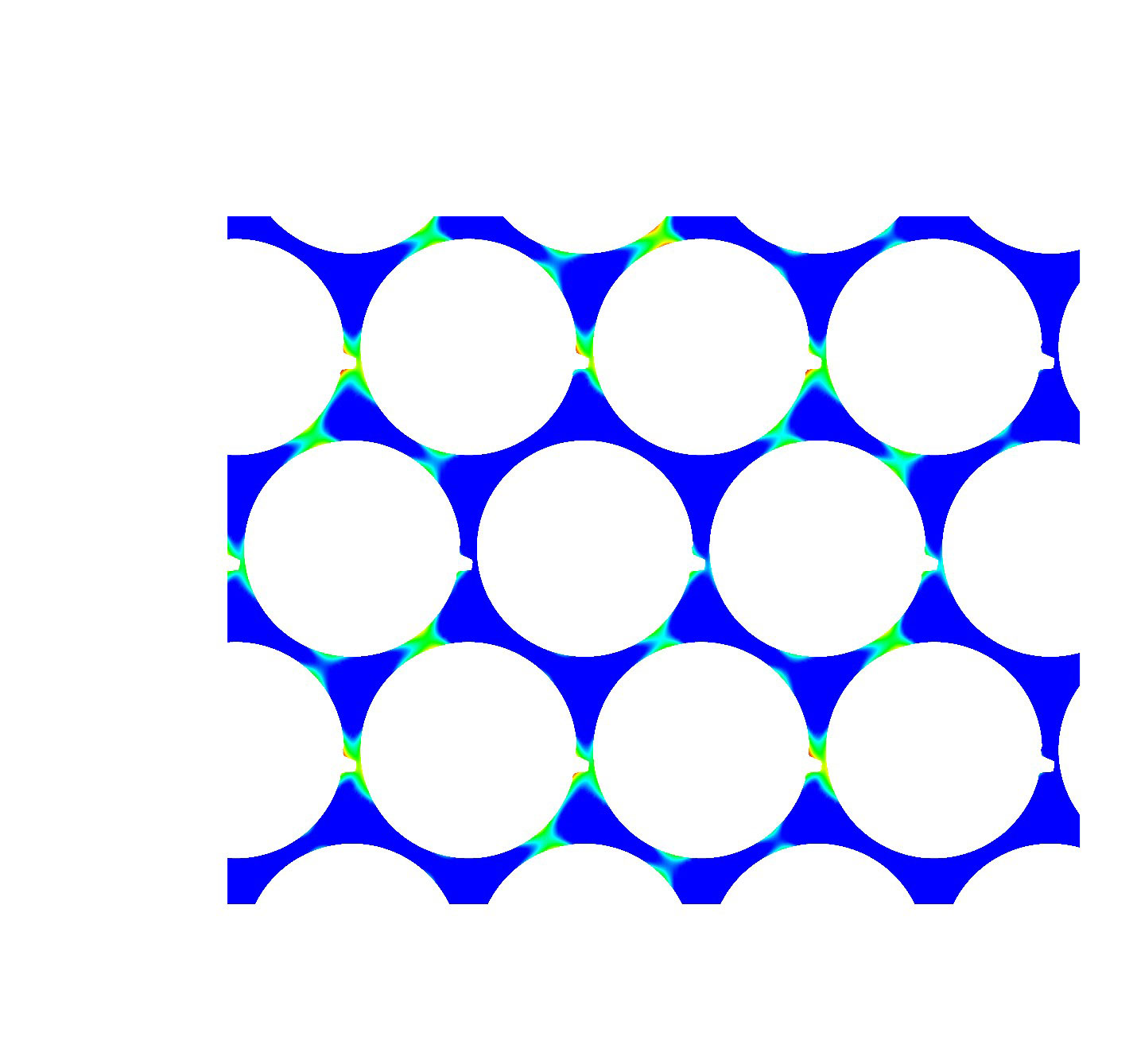
Engineers can model heat distribution in reactor designs with fewer or no approximations.
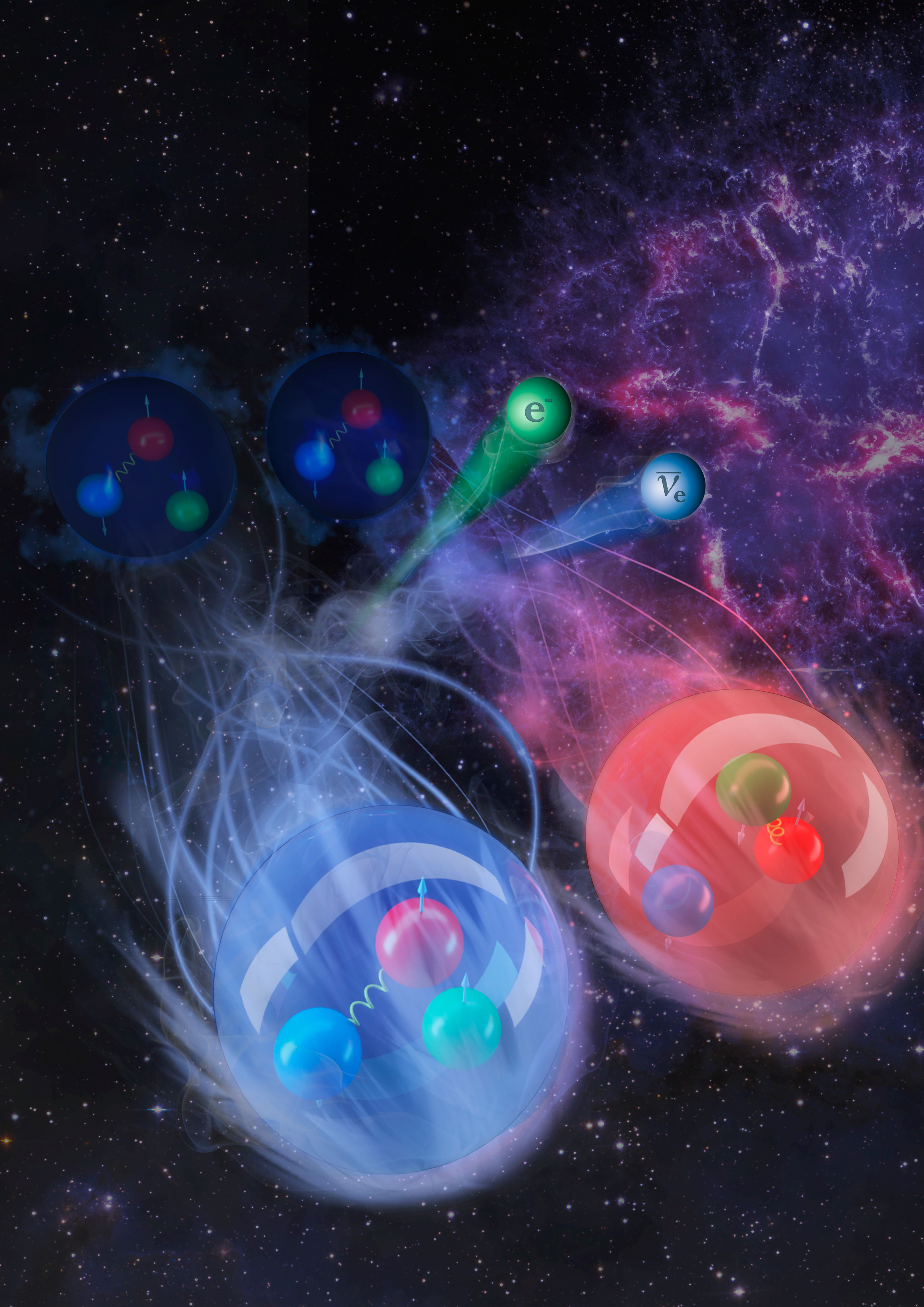

Researchers use advanced nuclear models to explain 50-year mystery surrounding the process stars use to transform elements.

Discovery of new boron-containing phase opens the door for resilient flexible electronics.

Materials prevent battery failure by inhibiting tree-like growths.
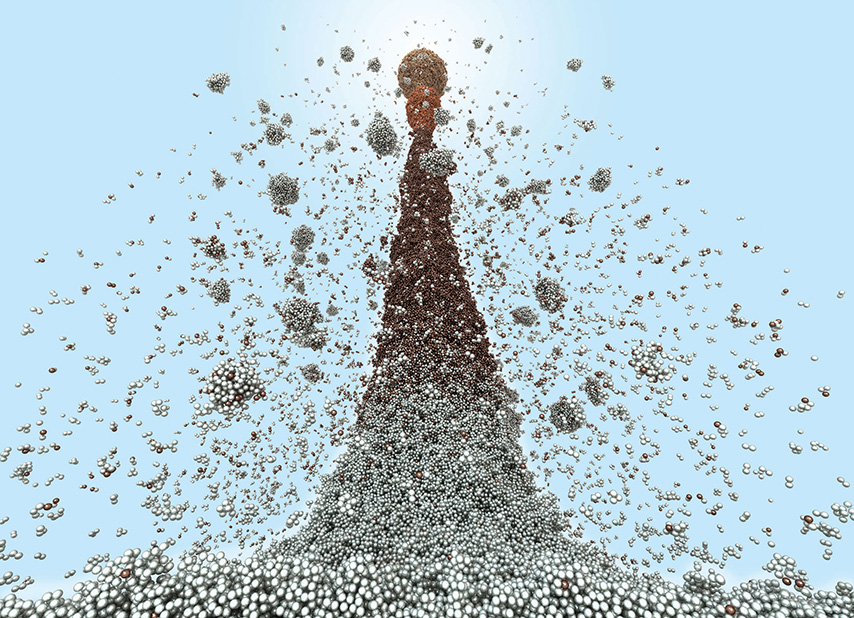

Titan supercomputer tells origin story of nanoparticle size distributions with large-scale simulations.

Neutron scattering reveals supersonic particles that carry heat and may improve electronics and sensors.
Read more about Beyond the “Sound Barrier” to Get the Heat Out
Researchers design self-assembling nanosheets that mimic the surface of cells.
Read more about Tiny, Sugar-Coated Sheets Selectively Target Pathogens
The Fusion Recurrent Neural Network reliably forecasts disruptive and destructive events in tokamaks.