
STAR Gains Access to “Wimpy” Quarks and Gluons
Low-momentum (wimpy) quarks and gluons contribute to proton spin, offering insights into protons’ behavior in all visible matter.

Low-momentum (wimpy) quarks and gluons contribute to proton spin, offering insights into protons’ behavior in all visible matter.

Researchers demonstrated record accelerating cavity performance using a technique that could lead to significant cost savings.

Beam chopper cuts accelerator-generated ion beams under highly demanding conditions.

Successful models of the fraught dynamics of two particle beams in close contact lead to smoother sailing in an area of particle acceleration.
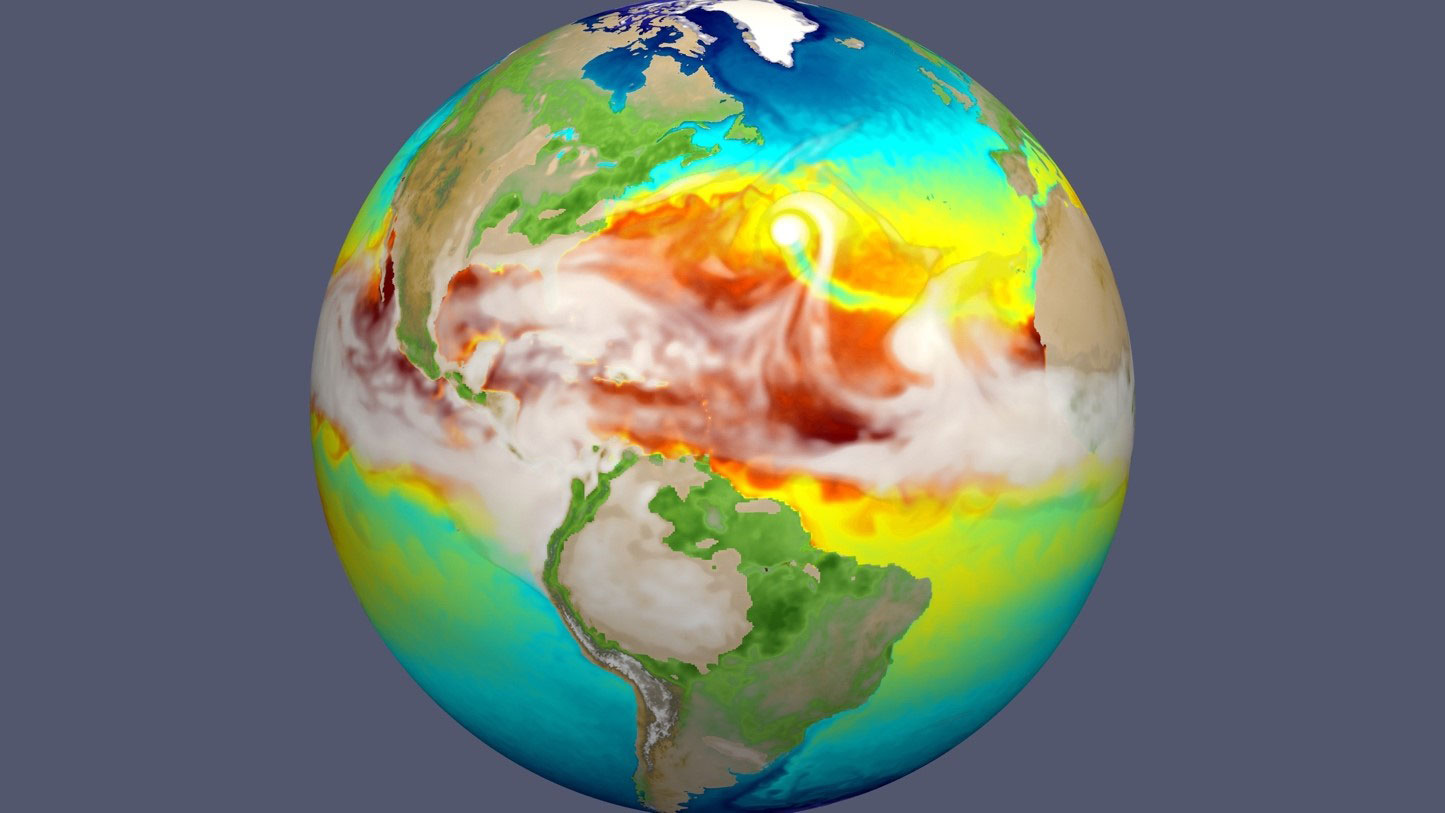
Scientists use supercomputers to determine how reliably a popular Earth system model represents precipitation regionally and globally.

A first-of-its-kind computer simulation reveals self-healing cement for geothermal and oil and gas wells performs better than originally thought.
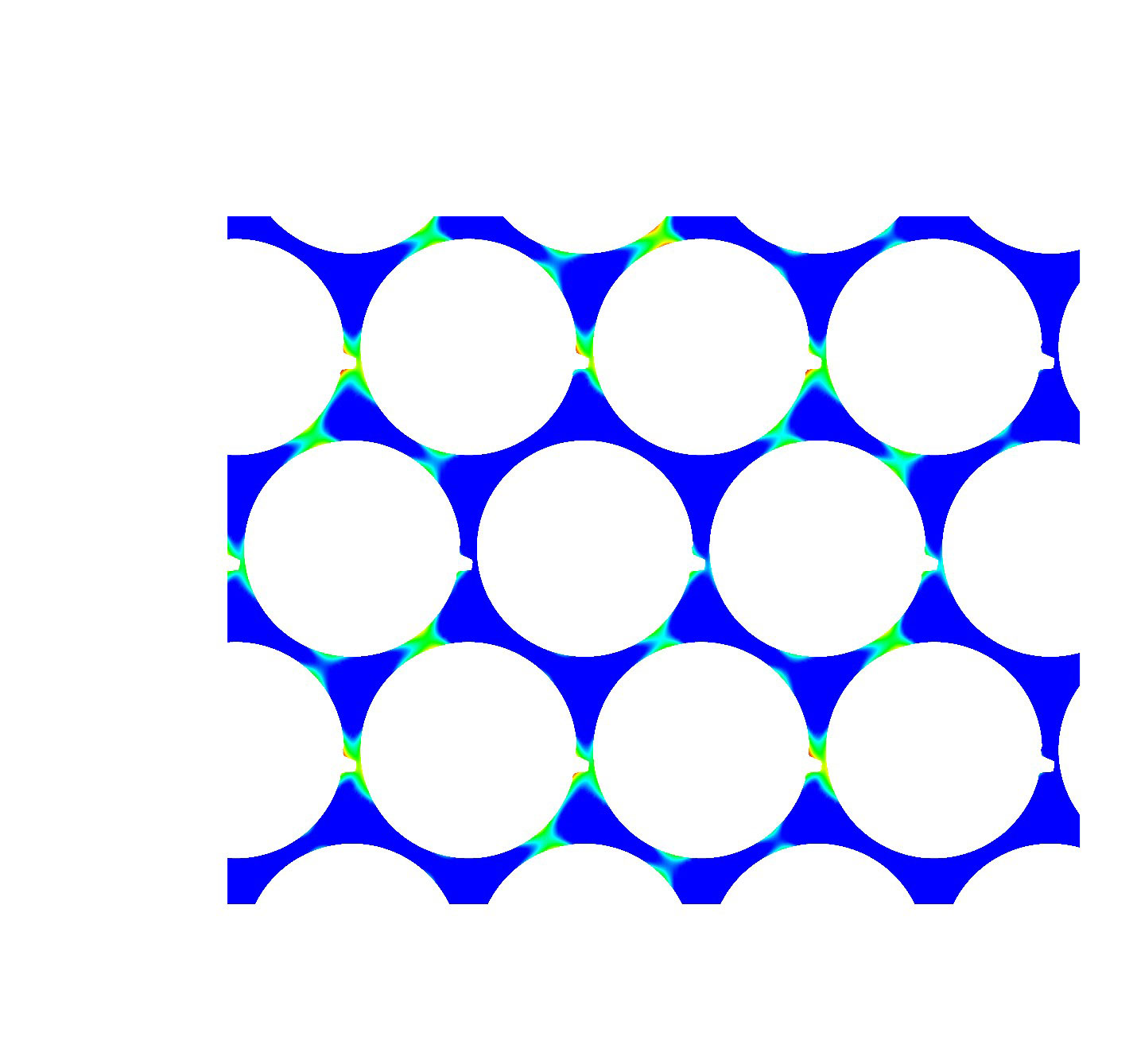
Engineers can model heat distribution in reactor designs with fewer or no approximations.
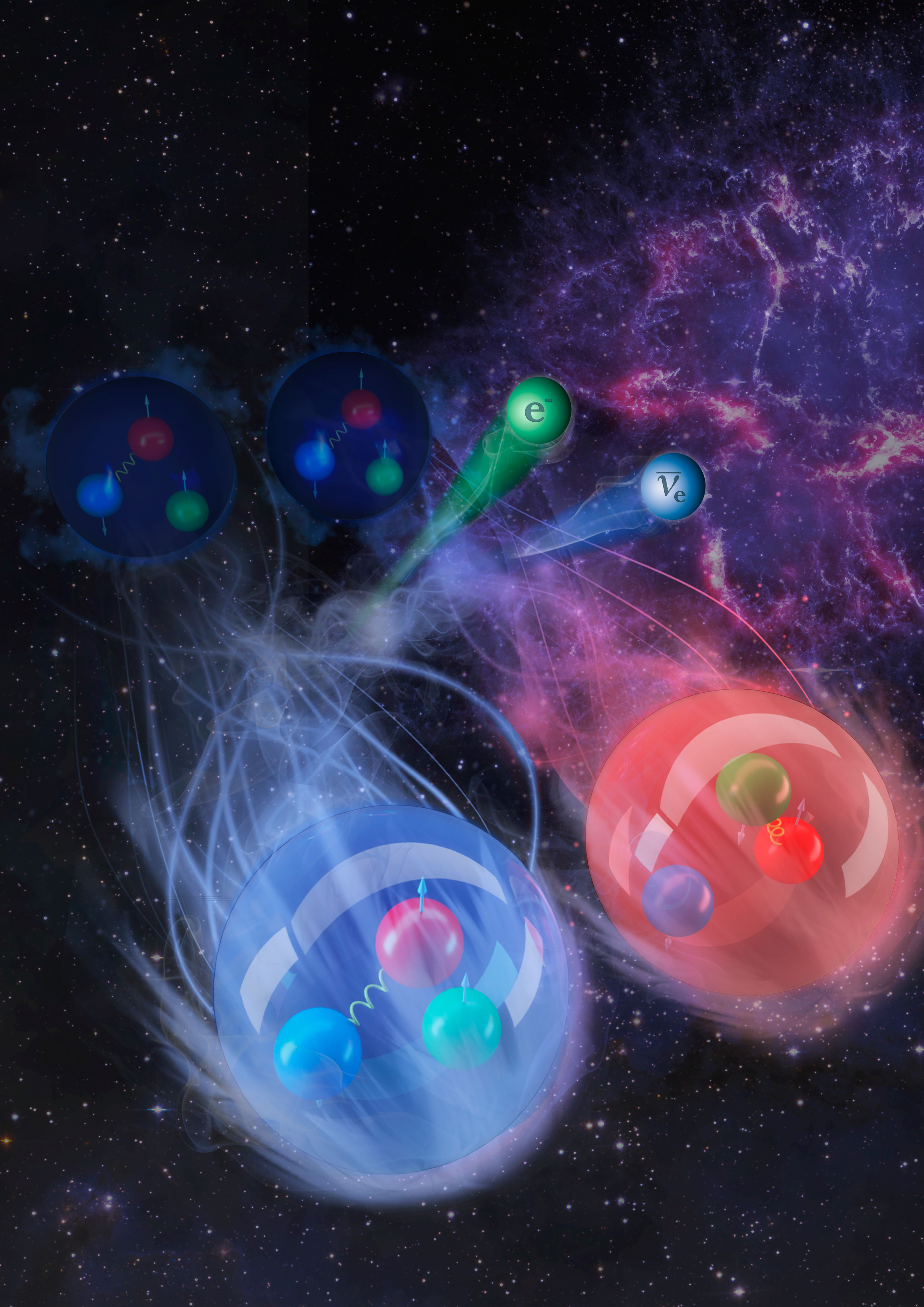

Researchers use advanced nuclear models to explain 50-year mystery surrounding the process stars use to transform elements.

A new route to make metal beneath a layer of graphite opens potentially new applications in solar cells and quantum computing.
Read more about Getting Metal Under Graphite’s Skin
Discovery of new boron-containing phase opens the door for resilient flexible electronics.

Researchers capture detailed images of polymers, using electron-based imaging and computer simulations.

New method could enable studying the fastest interactions of ultrabright X-rays with matter, a vital way of learning about chemical reactions.