
For Better Predictions, Researchers Evaluate Tropical Cyclone Simulation in the Energy Exascale Earth System Model
New analysis assesses the realism and biases of tropical cyclones at various resolutions in E3SM

New analysis assesses the realism and biases of tropical cyclones at various resolutions in E3SM

Natural emissions from living organisms drive new-particle formation in the atmosphere over the Amazon.

A new study seeks to improve reactive transport models by more accurately factoring in how bacteria move in groundwater.

To help researchers examine important cloud processes, a DOE user facility activity combines high-resolution simulations with real-world observations

Researchers found that soil drying altered metabolic pathways within soil microbial communities.

For the first time, an international team of scientists has discovered the true origin of sodium salt in pristine Amazon air.

Some cells stand firm against techniques to extract the biological material inside, while others don’t stand a chance.
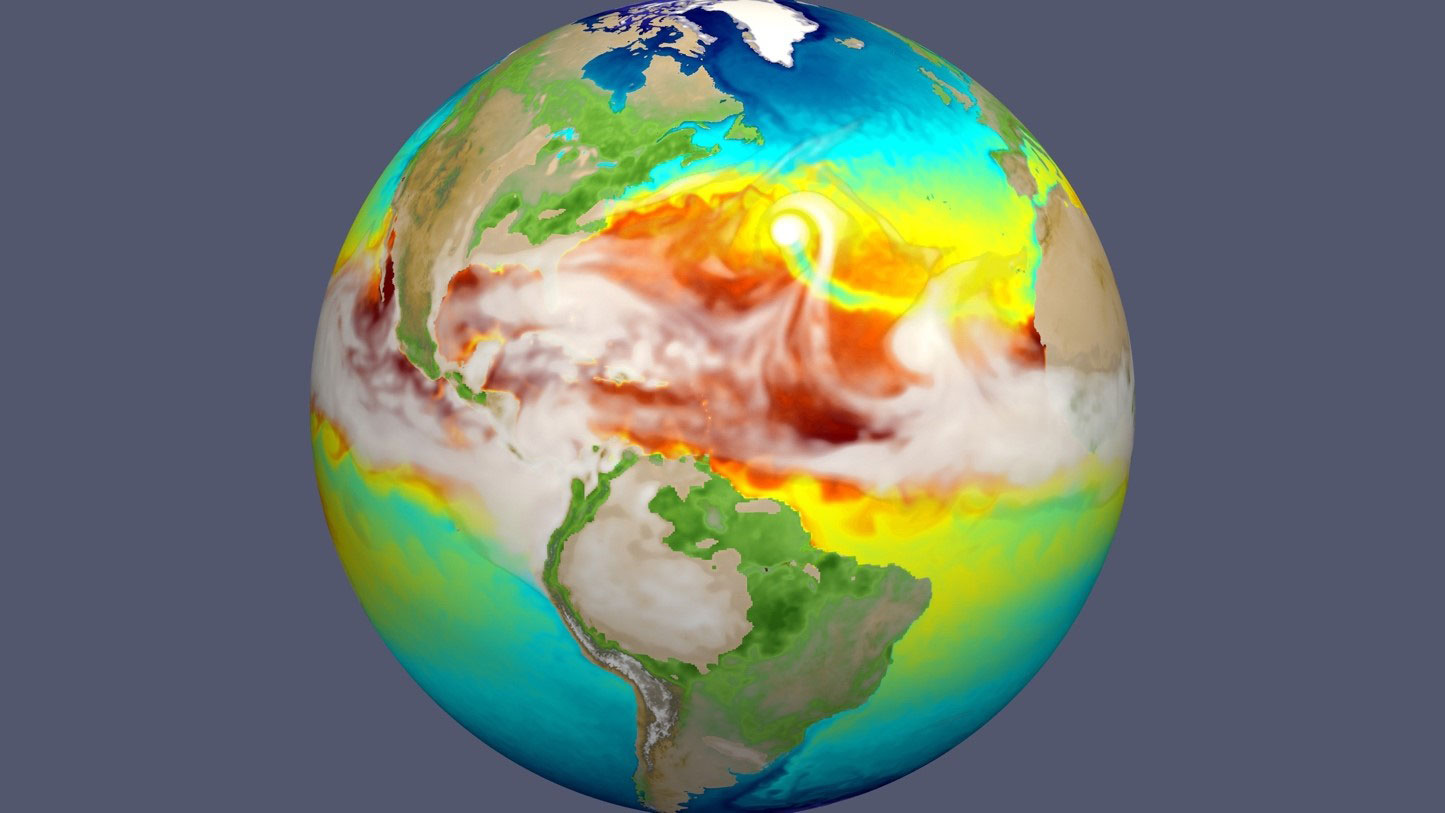
Scientists use supercomputers to determine how reliably a popular Earth system model represents precipitation regionally and globally.

Even a single species of bacteria can positively affect soils and plants, improving and even enabling agriculture in semi-arid areas.

First-of-a-kind study advances understanding of microbial and viral communities involved in biomass breakdown.

Scientists reveal the importance of an amino acid that supplies energy and protection for microbial communities deep underground.

An atomic view of how toxic uranium binds to iron minerals in the environment enables better predictions of its behavior.