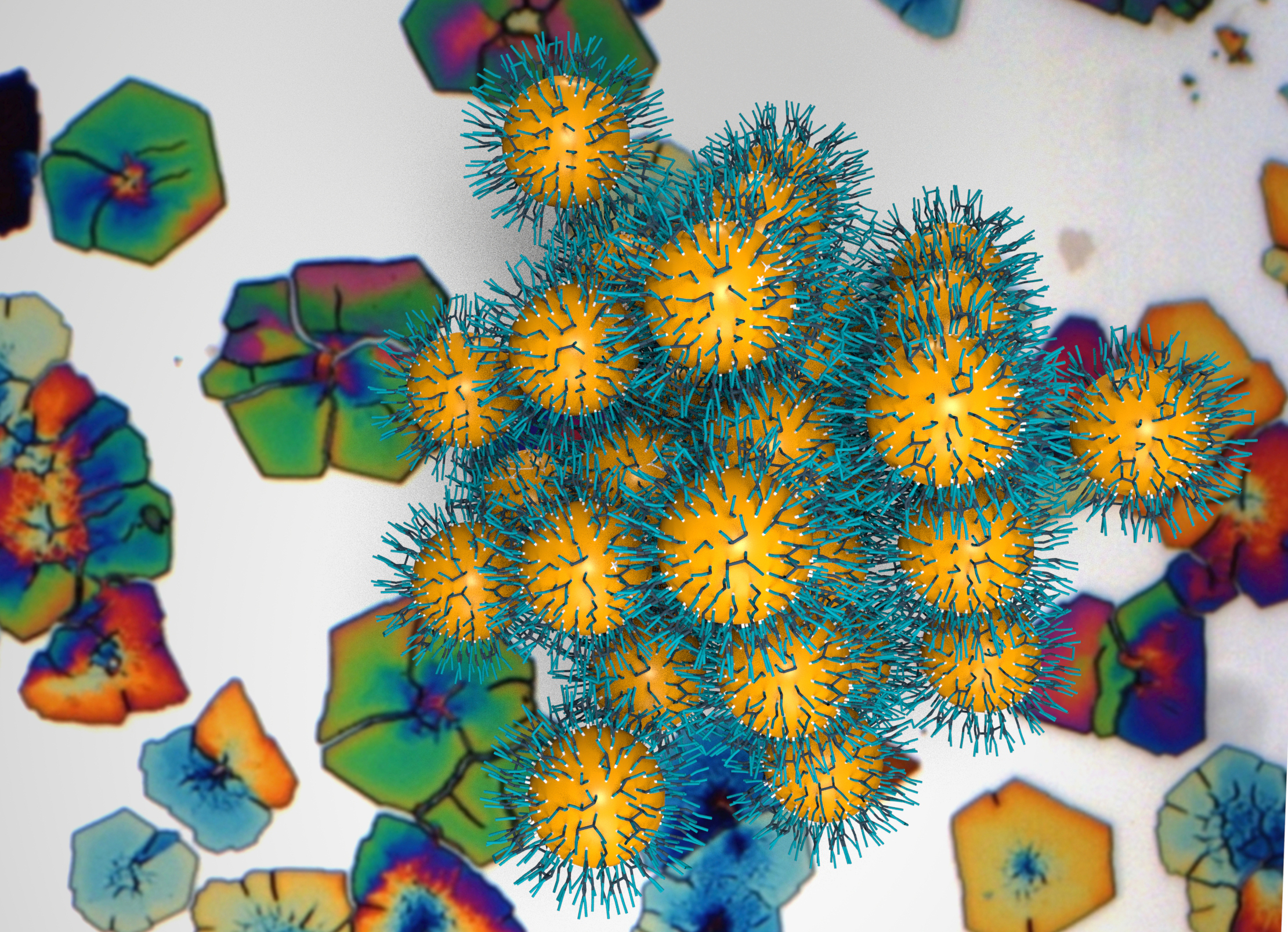
Super Nanoparticle Superlattices
Ligands allow fine tuning of nanoparticle superstructure properties

Ligands allow fine tuning of nanoparticle superstructure properties

New computer simulations reveal the explosive scene after ultra-dense stars collide, as well as where heavy elements may have originally formed.

Finding the right dyes for a new type of solar cell can be challenging, but this study used supercomputers to speed up the process

A new catalyst design meets cost, activity, and durability goals by leveraging ultralow loadings of platinum with platinum-free supports.

Scientists find the weak points to facilitate industrial applications of metallic glasses.

Ultrafast X-rays track how associated pairs of atoms find new locations when triggered by light.
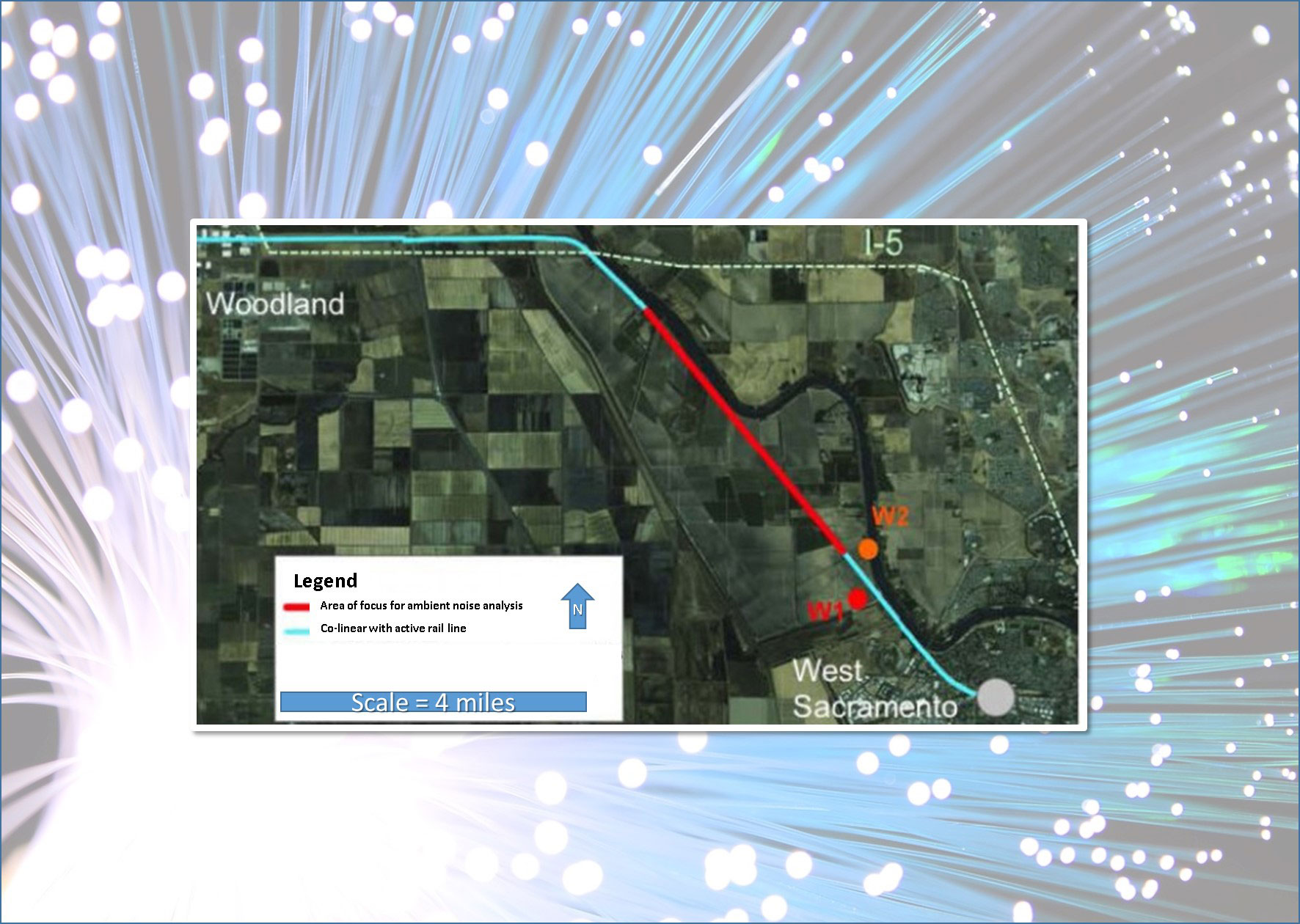
Dark fiber lays groundwork for long-distance earthquake detection and groundwater mapping.

Models use a fraction of the computational cost of today’s best atom-based water models.
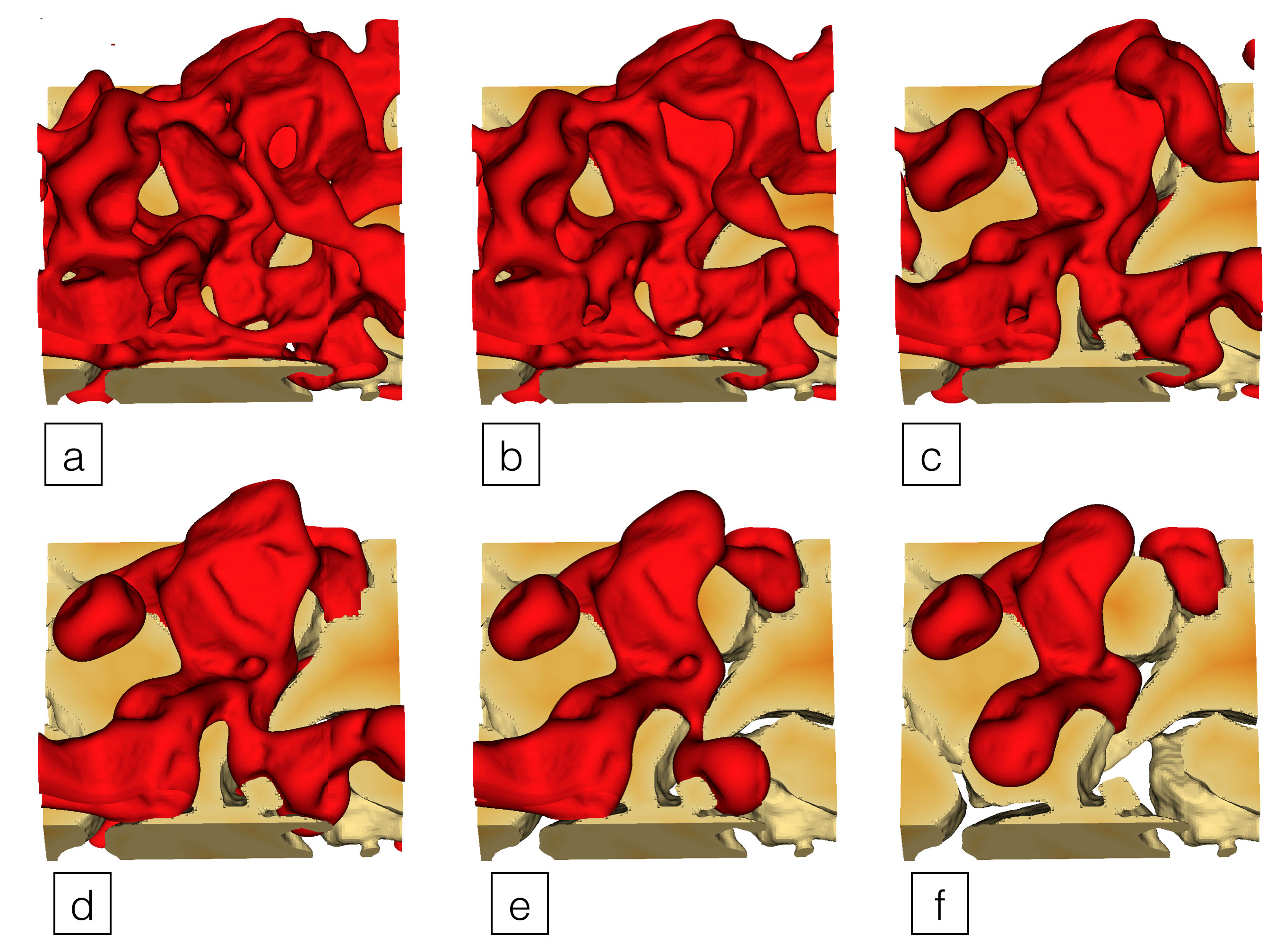
Supercomputer validates mathematical approach for describing geological features.

Low-momentum (wimpy) quarks and gluons contribute to proton spin, offering insights into protons’ behavior in all visible matter.
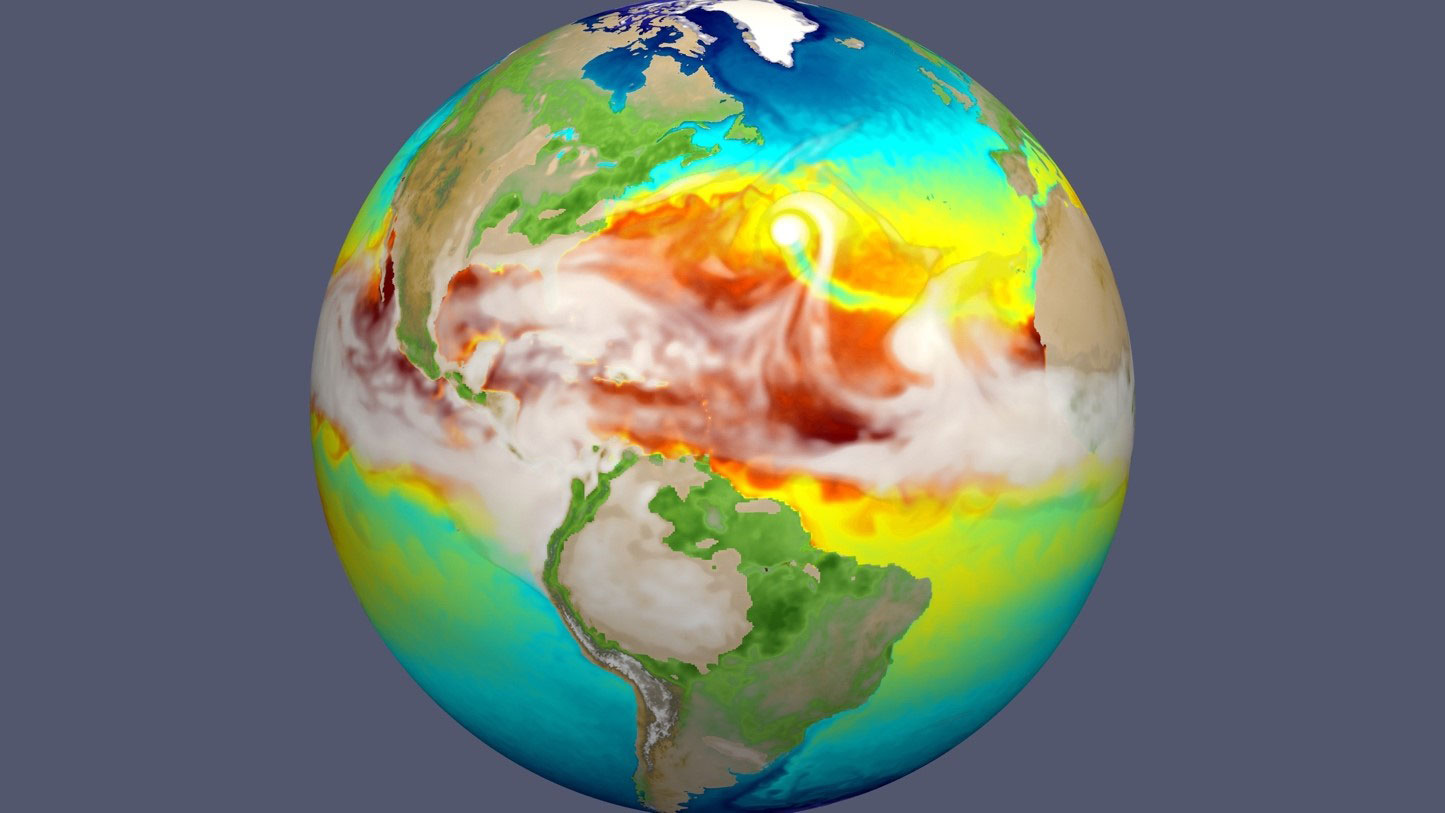
Scientists use supercomputers to determine how reliably a popular Earth system model represents precipitation regionally and globally.

A first-of-its-kind computer simulation reveals self-healing cement for geothermal and oil and gas wells performs better than originally thought.