
Superconducting Films for Particle Acceleration
Researchers demonstrated record accelerating cavity performance using a technique that could lead to significant cost savings.

Researchers demonstrated record accelerating cavity performance using a technique that could lead to significant cost savings.
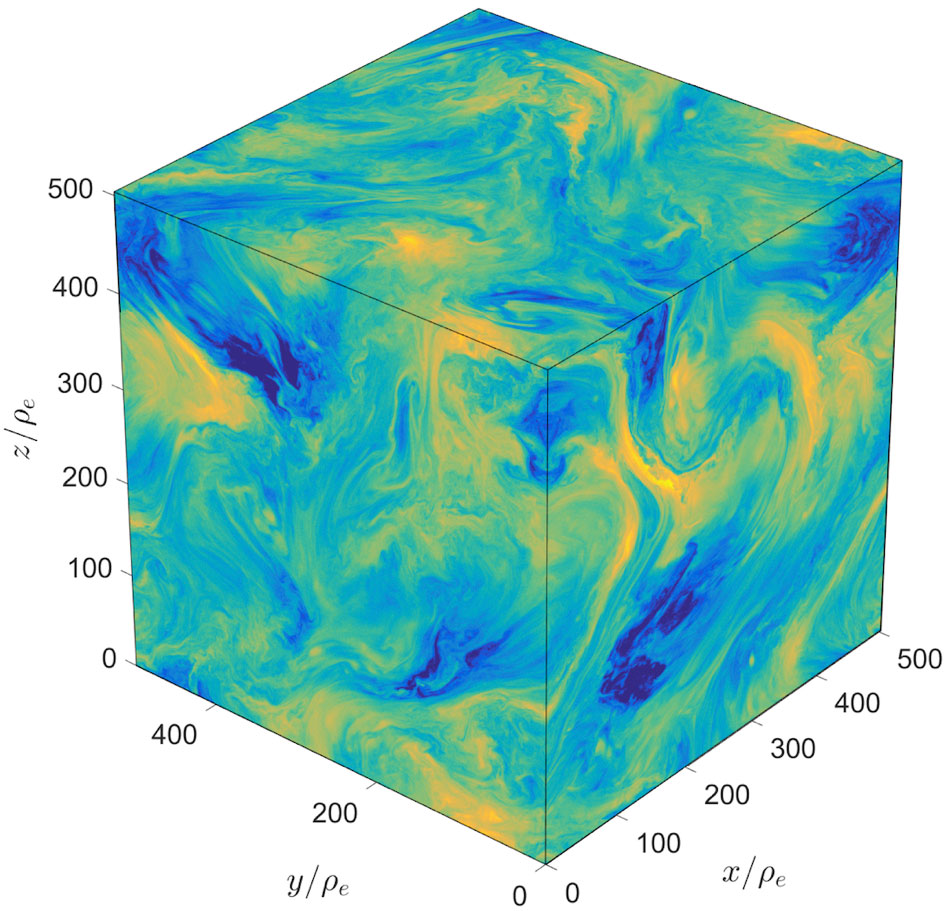
Particles act in a way that justifies extrapolating simulation results to astrophysical scales.

Discovery of new boron-containing phase opens the door for resilient flexible electronics.

Materials prevent battery failure by inhibiting tree-like growths.

The radii of three proton-rich calcium isotopes are smaller than previously predicted because models didn’t account for two nuclear interactions.
Read more about Why Are These Extremely Light Calcium Isotopes So Small?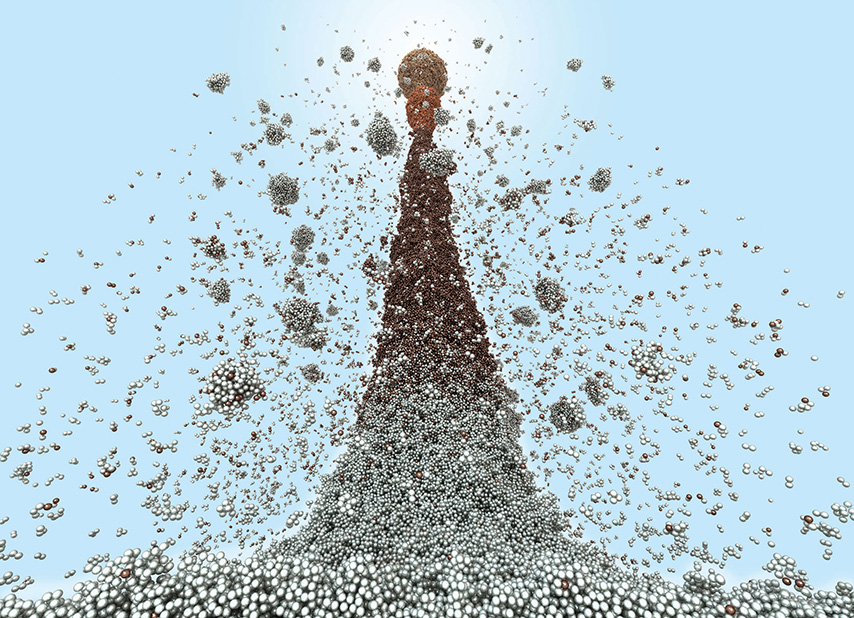
Titan supercomputer tells origin story of nanoparticle size distributions with large-scale simulations.

Scientists use software to "develop" images that trace neutrinos' interactions in a bath of cold liquid argon.

New method provides ultrafast switching of electronic structure and illuminates fundamentals of charge ordering, potentially offering a simple path for next-generation data storage.
Read more about Bursts of Light Shape Walls Between Waves of Charge
Detailed view of atoms opens doors for new designs to convert atomic displacements to electrical energy.
Read more about New Insights into a Long-Standing Debate About Materials that Turn Motion into Electricity
Researchers design self-assembling nanosheets that mimic the surface of cells.
Read more about Tiny, Sugar-Coated Sheets Selectively Target Pathogens
The Fusion Recurrent Neural Network reliably forecasts disruptive and destructive events in tokamaks.

Theorists show how a new quantum device could control a chemical reaction remotely, changing our understanding of how reactions can work.