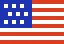
Energy Flow Diagram

This diagram shows 2010 energy flow from primary sources (oil, natural gas, coal, nuclear, and renewables) through transformations (electricity
generation) to end uses (transportation, industry, and residential, and commercial sectors). Oil provided the largest share of the 98 quads of primary energy
consumed, and most of it was used for transportation. Consumption of natural gas, the nation's second largest energy source, is split three ways—electricity
generation, industrial processing, and residential and commercial uses (mostly for heating). Coal, our third largest source, is used almost exclusively for
electricity. Nuclear energy and renewables each meet less than 10% of U.S. energy demand. Data are from the U.S. Energy Information Administration's Annual
Energy Review (www.eia.gov/aer/) and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (flowcharts.llnl.gov). Higher Resolution Image )
Quick Facts, U.S. Energy Flow

Higher Resolution Image
98 QUADS ANNUAL U.S. ENERGY CONSUMPTION
A quad represents
a quadrillion British thermal units (Btu), equal to 172 million barrels of oil, 50 million tons of coal, or 1 trillion cubic feet of natural gas.
2010 Energy Supply, 98 Quads
75 Quads from domestic production
23 Quads from net imports
|

19 MILLION BARRELS OF OIL CONSUMED DAILY
At $100 per barrel, this is roughly $2 billion of oil each day. 71% of U.S. oil consumption is for
transportation. The U.S. imports 50% of the oil it uses, more than any other country.

83 PERCENTAGE OF ENERGY FROM FOSSIL FUELS
Most of our energy supply comes from nonrenewable, carbon-intensive fossil fuels: oil, natural gas, and coal. Coal is the largest domestically produced energy source, but its use releases more CO2 per unit of energy compared to that
for oil or natural gas.

104 NUCLEAR REACTORS
Located at 65 nuclear plants, 104 reactors provide almost 20% of the total net electricity generated in the U.S. Although the newest reactor entered commercial service in 1996, the U.S. generates more nuclear energy than any other country.

10 PERCENTAGE OF ELECTRICITY FROM RENEWABLES
Biomass and hydropower are the most heavily used renewable energy sources. For U.S. electricity generation, hydropower is the largest renewable source (6%), with wind, biomass, geothermal, and solar each providing about 1% or less.
2010 Energy Conversion, 98 Quads
58 Quads from direct use of primary supplies
40 Quads are consumed to generate electricity
|

160,000 MILES OF POWER LINES IN U.S. ELECTRIC GRID
This "grid" of high-voltage transmission lines consists of three large interconnected systems with more than 10,000 generating units and 3,200 electric distribution utilities. About two-thirds of the 40 quads used to generate, transmit, and distribute electricity is lost at power plants and in power lines, resulting in 13 quads of utilized electricity
2010 U.S. Energy Consumption, 98 Quads
42 Quads are used energy
56 Quads are lost during conversion
|

3 TRILLION MILES TRAVELED ANNUALLY
Some 235 million cars and light trucks covered most of the 3 trillion highway miles traveled in the U.S. each year. Light-duty vehicles use 60% of U.S. transportation energy. Heavy trucks (18%), aircraft (9%), and boats and ships (5%) account for most of the rest.

32 PERCENTAGE OF INDUSTRIAL ENERGY FOR REFINING
Petroleum refining is the largest industrial consumer of energy. Other energy-intensive industries include chemical (24%), paper (11%), and metal (8%) manufacturing.

113 MILLION HOMES USE 22% OF U.S. ENERGY
Space and water heating account for more than half of residential energy use. The typical U.S. family spends $2,000 a year on home utility bills.
77 PERCENTAGE OF COMMERCIAL ENERGY FROM ELECTRICITY
There are roughly 5.3 million commercial buildings in the U.S., including shopping malls and other retail space, offices, schools, hospitals, warehouses, and hotels. Lighting is the largest consumer of electricity in commercial properties and a key target for energy savings.